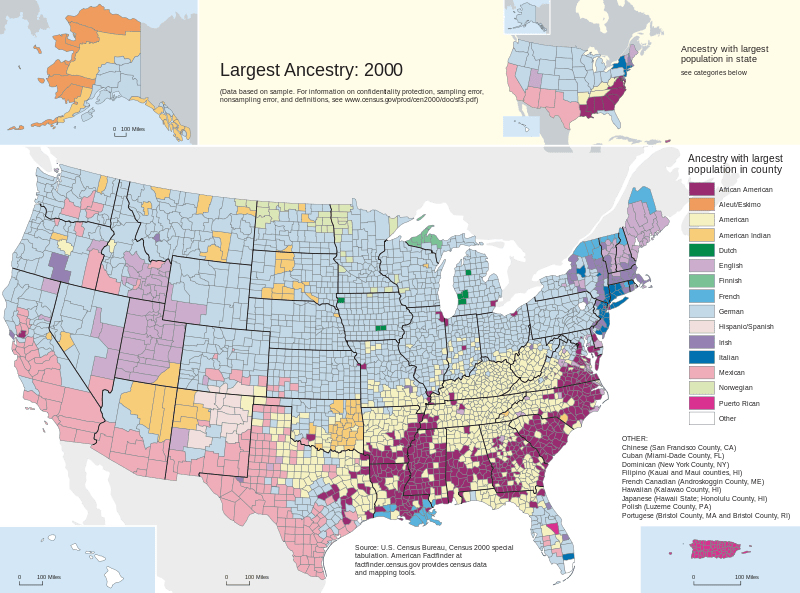
Complementarity example ap human geography is a multifaceted concept that explores the ways in which different elements or entities interact and enhance one another. In the realm of human geography, complementarity manifests in various forms, ranging from economic activities to cultural exchanges and environmental interactions.
This concept provides a framework for understanding how diverse factors converge to create a cohesive and dynamic human landscape. By examining complementarity, we gain insights into the intricate relationships that shape our world and the potential for collaboration and sustainable development.
Economic Complementarity: Complementarity Example Ap Human Geography
Economic complementarity refers to the mutually beneficial relationship between two or more economic activities that enhance each other’s productivity or value. This phenomenon manifests in various geographic contexts, such as:
- Agriculture and manufacturing:Farmers produce raw materials that are processed by manufacturers, creating a symbiotic relationship.
- Tourism and hospitality:Tourists generate demand for services such as accommodation, dining, and entertainment, supporting the local economy.
- International trade:Countries specialize in producing goods and services that they have a comparative advantage in, leading to mutually beneficial trade relationships.
Specialization and Trade, Complementarity example ap human geography
Specialization and trade play a crucial role in fostering economic complementarity. When regions or countries specialize in producing goods and services that they are most efficient at, they can produce a surplus and trade with others to obtain goods and services that they cannot produce efficiently.
- Comparative advantage:The principle that countries should specialize in producing goods and services where they have a lower opportunity cost.
- Free trade agreements:Agreements between countries to reduce or eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers, promoting specialization and trade.
Real-World Examples
- China and the United States:China specializes in manufacturing goods, while the United States specializes in services and technology. This complementarity has led to a mutually beneficial trade relationship.
- European Union:Member states have specialized in different industries, creating a highly integrated economic zone with significant complementarity.
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):Countries within ASEAN have complementary economies, with some specializing in agriculture, others in manufacturing, and others in tourism.
Question Bank
What is the significance of complementarity in economic development?
Complementarity in economic development allows regions or countries to specialize in producing goods or services that they have a comparative advantage in. This specialization leads to increased efficiency, lower costs, and expanded trade opportunities, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
How does cultural complementarity contribute to societal well-being?
Cultural complementarity promotes understanding, appreciation, and respect for diverse cultures. It encourages cultural exchange and interaction, leading to a richer and more vibrant society. Cultural complementarity fosters creativity, innovation, and a sense of global interconnectedness.
Why is environmental complementarity crucial for sustainable development?
Environmental complementarity emphasizes the interdependence of natural resources and ecosystems. It highlights the need to maintain ecological balance and preserve biodiversity. By recognizing the complementarity between human activities and the environment, we can promote sustainable practices and ensure the long-term health of our planet.