Delving into the realm of fluid pressure, this meticulously crafted article serves as a beacon of knowledge for those seeking to unravel the mysteries of this captivating subject. Section 13.1 Fluid Pressure Pages 390-393 Answer Key stands as a testament to the boundless applications of fluid pressure, from the depths of engineering to the wonders of everyday life.
Within these pages, readers will embark on an enlightening journey, exploring the fundamental principles that govern fluid pressure. Through a comprehensive examination of measurement techniques, practical applications, and its profound impact on our daily existence, this guide empowers individuals to grasp the intricacies of fluid pressure with newfound clarity.
Fluid Pressure: Section 13.1 Fluid Pressure Pages 390-393 Answer Key
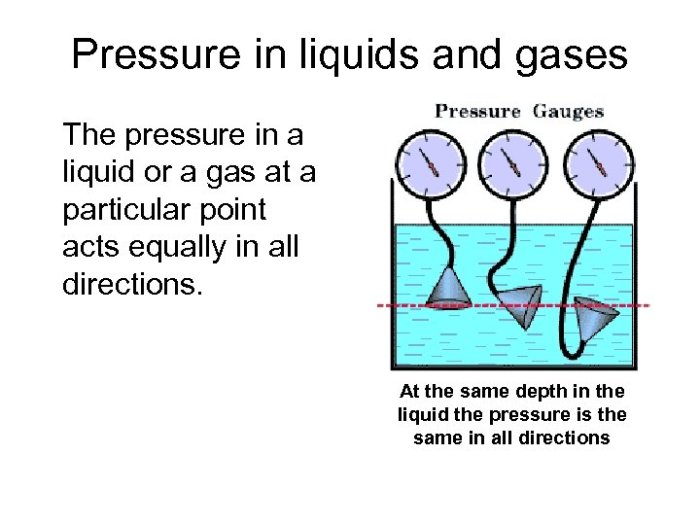
Fluid pressure refers to the force exerted by a fluid (liquid or gas) per unit area. It arises from the weight of the fluid and its tendency to flow from regions of high pressure to low pressure. Fluid pressure plays a crucial role in various scientific disciplines and technological applications.
Examples of fluid pressure in real-world applications include the pressure exerted by water in a water tank, the air pressure in a car tire, and the blood pressure in our arteries. These examples demonstrate the diverse ways in which fluid pressure affects our daily lives.
The factors that affect fluid pressure include the density of the fluid, the depth of the fluid, and the acceleration due to gravity. These factors determine the magnitude and direction of the fluid pressure at a given point.
Measuring Fluid Pressure
There are several methods used to measure fluid pressure, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include:
- Manometers: Manometers use the height of a fluid column to measure pressure. They are simple and inexpensive, but their accuracy can be affected by temperature and fluid density.
- Pressure gauges: Pressure gauges use a mechanical or electronic sensor to measure pressure. They are more accurate than manometers, but they can be more expensive.
- Pressure transducers: Pressure transducers convert fluid pressure into an electrical signal. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including medical and industrial settings.
Applications of Fluid Pressure, Section 13.1 fluid pressure pages 390-393 answer key
Fluid pressure has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Hydraulic systems: Hydraulic systems use fluid pressure to transmit power. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including construction equipment, industrial machinery, and automotive brakes.
- Pneumatic systems: Pneumatic systems use air pressure to transmit power. They are used in a variety of applications, including air tools, robotics, and medical equipment.
- Hydrostatic testing: Hydrostatic testing uses fluid pressure to test the integrity of pipes, tanks, and other pressure vessels.
Fluid Pressure in Daily Life
Fluid pressure plays a role in many everyday activities, such as:
- Water distribution: Fluid pressure is used to distribute water throughout homes and businesses. The pressure of the water in your faucet is determined by the height of the water tower or reservoir that supplies your water.
- Blood pressure: Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by blood on the walls of blood vessels. It is an important indicator of overall health and can be used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as hypertension.
- Weather forecasting: Fluid pressure is used to measure atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure is an important factor in weather forecasting and can be used to predict the likelihood of storms and other weather events.
Essential Questionnaire
What is fluid pressure?
Fluid pressure is the force exerted by a fluid per unit area.
How is fluid pressure measured?
Fluid pressure can be measured using various methods, including manometers, pressure gauges, and transducers.
What factors affect fluid pressure?
Fluid pressure is affected by factors such as depth, density, and acceleration.
What are some applications of fluid pressure?
Fluid pressure has numerous applications in fields such as hydraulics, pneumatics, and fluid power.
How does fluid pressure impact daily life?
Fluid pressure plays a crucial role in various aspects of daily life, including water distribution, transportation, and medical devices.

