A nurse is preparing to administer phenytoin suspension 300 mg – A nurse preparing to administer phenytoin suspension 300 mg embarks on a critical task that demands meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of the medication’s properties and potential effects. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of patient assessment, medication preparation, administration techniques, monitoring and evaluation, and patient education, providing healthcare professionals with an authoritative resource to ensure safe and effective administration of phenytoin suspension.
Phenytoin suspension, an anticonvulsant medication, plays a vital role in managing various seizure disorders. Understanding its mechanism of action, potential side effects, and appropriate administration techniques is paramount for nurses to deliver optimal patient care.
Phenytoin Suspension Administration: A Comprehensive Guide for Nurses: A Nurse Is Preparing To Administer Phenytoin Suspension 300 Mg
Phenytoin suspension is a medication used to treat seizures and other neurological conditions. Nurses play a vital role in ensuring the safe and effective administration of this medication. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the nursing responsibilities involved in phenytoin suspension administration, including patient assessment, medication preparation, administration techniques, monitoring and evaluation, and patient education.
Patient Assessment, A nurse is preparing to administer phenytoin suspension 300 mg
Before administering phenytoin suspension, nurses must assess the patient’s condition to identify any potential contraindications or precautions. This assessment includes:
- Vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature)
- Neurological status (level of consciousness, orientation, reflexes)
- Cardiac status (ECG, history of heart disease)
- Hepatic function (liver enzymes)
- Renal function (serum creatinine)
Potential contraindications to phenytoin suspension administration include severe liver disease, severe heart disease, and hypersensitivity to the medication.
Medication Preparation
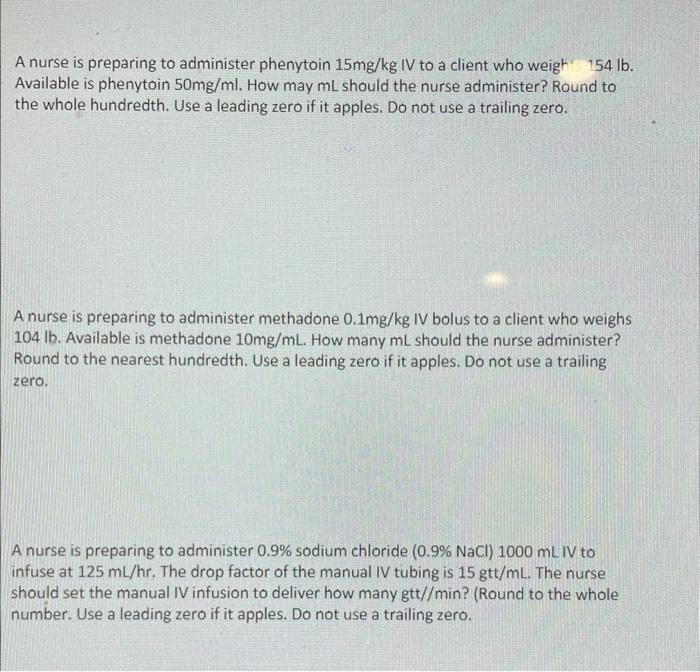
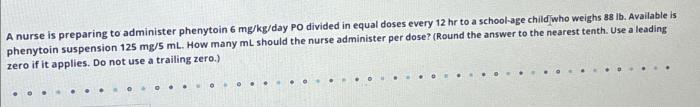
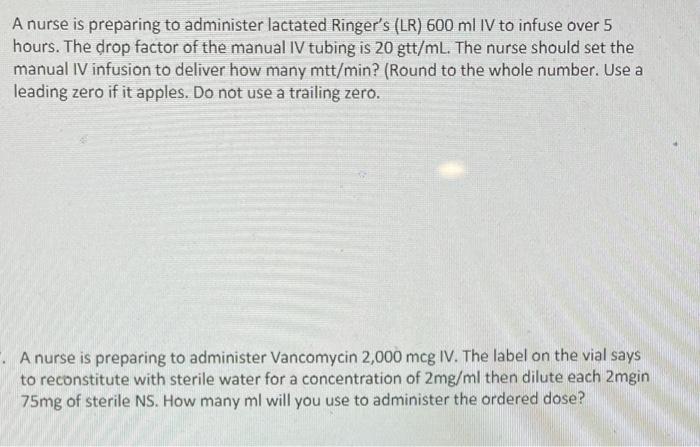
Phenytoin suspension is available in different strengths and concentrations. Nurses must calculate the correct dosage based on the patient’s weight or other factors, as prescribed by the healthcare provider.
To prepare phenytoin suspension, the nurse should:
- Shake the bottle thoroughly to ensure uniform suspension.
- Use an oral syringe to withdraw the prescribed dose.
- Administer the medication immediately after preparation.
Administration Techniques
Phenytoin suspension can be administered orally or intravenously (IV). The route of administration depends on the patient’s condition and the healthcare provider’s orders.
For oral administration, the nurse should:
- Administer the medication with a full glass of water.
- Instruct the patient to swallow the medication whole, without chewing or crushing.
For IV administration, the nurse should:
- Dilute the medication in normal saline or dextrose 5% in water.
- Administer the medication slowly over 30 minutes.
- Monitor the patient closely for any adverse reactions.
Monitoring and Evaluation
After administering phenytoin suspension, nurses should monitor the patient’s response to the medication. This includes:
- Assessing for therapeutic effects (e.g., seizure control)
- Monitoring for adverse reactions (e.g., nausea, vomiting, dizziness)
- Regular blood level monitoring to ensure therapeutic levels
Nurses should also assess the patient’s adherence to the medication regimen and provide education on the importance of follow-up appointments.
Patient Education
Nurses play a crucial role in educating patients about phenytoin suspension. This education should include:
- Dosage and administration schedule
- Potential side effects and how to manage them
- Importance of adherence and follow-up appointments
- Dietary restrictions (e.g., avoid grapefruit juice)
- Precautions to take while taking phenytoin suspension (e.g., avoid alcohol)
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary indication for phenytoin suspension?
Phenytoin suspension is primarily indicated for the treatment of various seizure disorders, including generalized tonic-clonic seizures, focal seizures, and status epilepticus.
What are the potential side effects of phenytoin suspension?
Potential side effects of phenytoin suspension include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and nystagmus. In rare cases, more severe side effects such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and hepatic toxicity may occur.
How should phenytoin suspension be stored?
Phenytoin suspension should be stored at room temperature, protected from light. It should not be refrigerated or frozen.